The Origin of Copper: Unveiling the Story of a Versatile Element

Copper, a red-orange metal known for its excellent conductivity and malleability, has been valued by ancient civilizations for thousands of years. It is a key component in various industrial applications, including electrical wiring, construction materials, and electronic devices. Understanding the origin of copper, its natural occurrence, extraction process, commercial processing, and the impact of mining on the environment paints a comprehensive picture of this vital element.
Copper does not typically occur in nature as a pure element. Instead, it is found in ores, usually in combination with other elements such as sulfur, oxygen, and iron. The most common ores containing copper are chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) and bornite (Cu5FeS4). These ores are mainly located in regions with volcanic activity or in sedimentary rocks formed through millions of years of geological processes.
The mining process for extracting copper from its ores is complex and involves several stages. Initially, prospecting is conducted to identify potential copper-rich areas. Once a suitable site is found, mining companies remove the overlying rock and soil to access the ore deposits. This process can involve open-pit mining or underground mining, depending on the quality and depth of the ore.
After the ore is extracted, it undergoes a series of physical and chemical processes to separate the copper from other elements. Initially, the ore goes through crushing and grinding to reduce its size. It is then treated with chemicals that break down the ore into a slurry, allowing for the separation of copper and other minerals. Various techniques, such as flotation and smelting, are employed to further purify the copper concentrate.
Once the copper is extracted from the ore and processed into a raw material known as blister copper, it is sent to refineries for commercial processing. The refining process involves removing impurities through electrolysis or other methods. The final product is high-purity copper cathodes, which are used as a raw material for numerous industries.
Several countries are significant players when it comes to copper production and mining. Chile, the world’s largest copper producer, accounts for approximately one-third of global copper output. Other major producers include Peru, China, the United States, and Australia. The abundance of copper in Chile and other copper-rich regions has substantial economic implications for these countries, providing a significant share of their export revenues.
Although copper mining is economically significant, it is not without environmental consequences. Mining operations can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Waste materials, including rock fragments and contaminated water, can damage surrounding ecosystems and impact the health of local wildlife. Additionally, extraction processes release greenhouse gases and other air pollutants, contributing to climate change and air pollution.
To mitigate these issues, responsible mining practices are crucial. In recent years, regulations and industry standards have aimed to minimize the environmental impact of copper mining. Companies are required to adopt sustainable practices, such as reclamation and rehabilitation of mined areas, water treatment systems, and reducing emissions. However, there is still much work to be done to ensure that mining activities do not compromise the delicate balance of our natural environment.
Commercially, copper has a wide range of applications across various sectors. Its excellent electrical conductivity makes it an essential component in power transmission and electrical wiring. Copper is also used in construction materials, such as pipes and roofing, due to its corrosion resistance. Moreover, it plays a vital role in the manufacturing of electronic devices, such as smartphones, computers, and televisions.
China is the largest producer of refined copper, followed by Chile and Japan. These countries have established extensive copper smelting and refining capacities to meet the growing demand for the metal from both domestic and international markets. The commercial production of copper plays a crucial role in these countries’ economic growth and export revenue, contributing to their overall development.
In conclusion, copper, a versatile metal with numerous industrial applications, is not found in nature as a pure element. It occurs in ores and is extracted through a complex mining process involving several stages. Responsible mining practices are essential to mitigate the environmental impact of mining operations. Chile is the largest copper producer globally, and other significant producers include Peru, China, the United States, and Australia. Commercial processing of copper involves refining the extracted metal into high-purity copper cathodes. The commercial production of copper contributes significantly to the economy of producing countries and their global export revenue. Nonetheless, sustainable practices need to be implemented to ensure the long-term environmental sustainability of the copper mining industry.
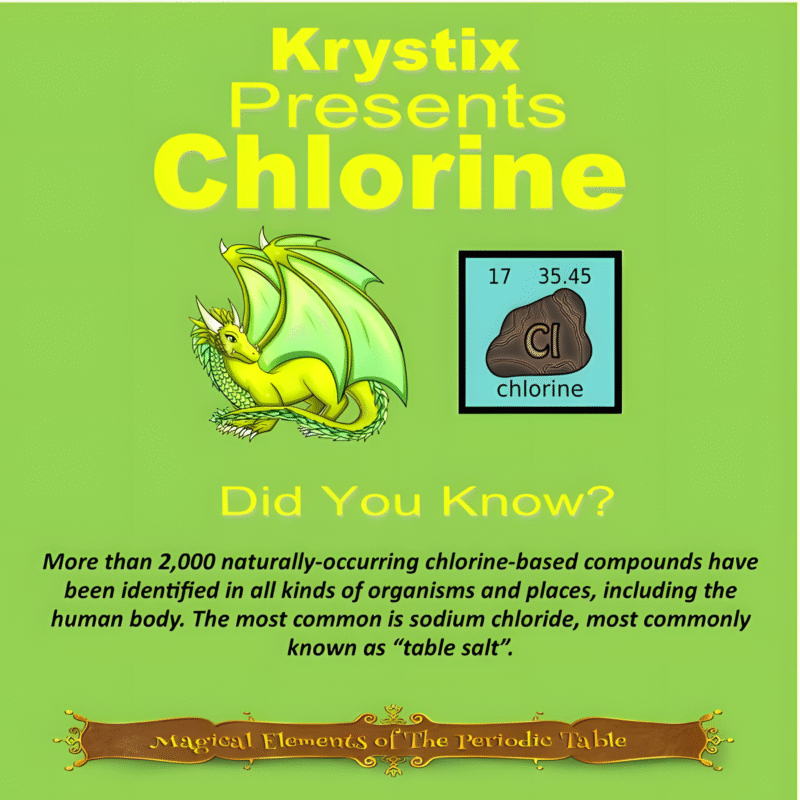
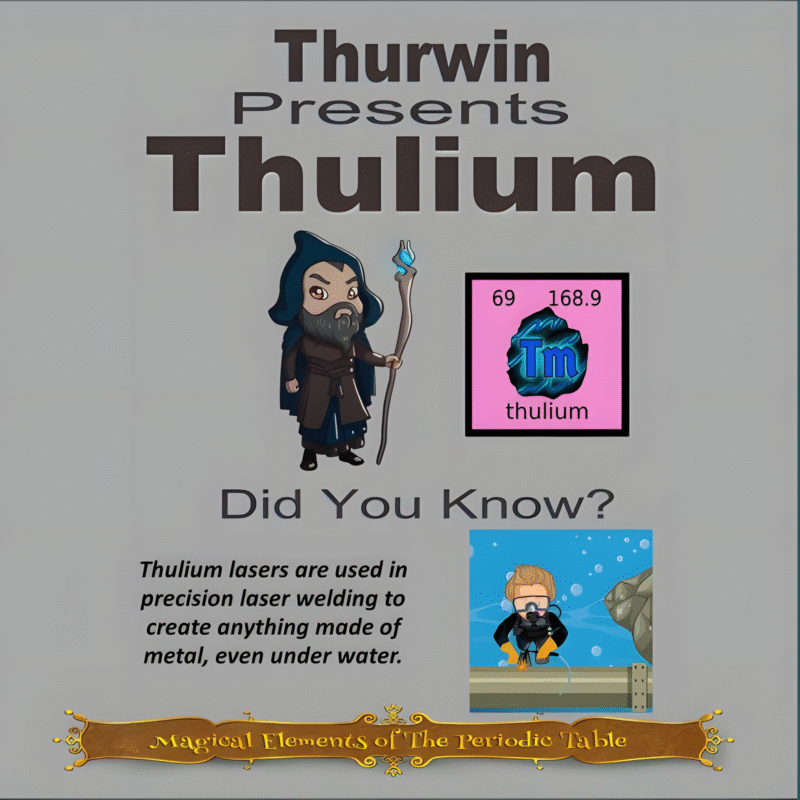
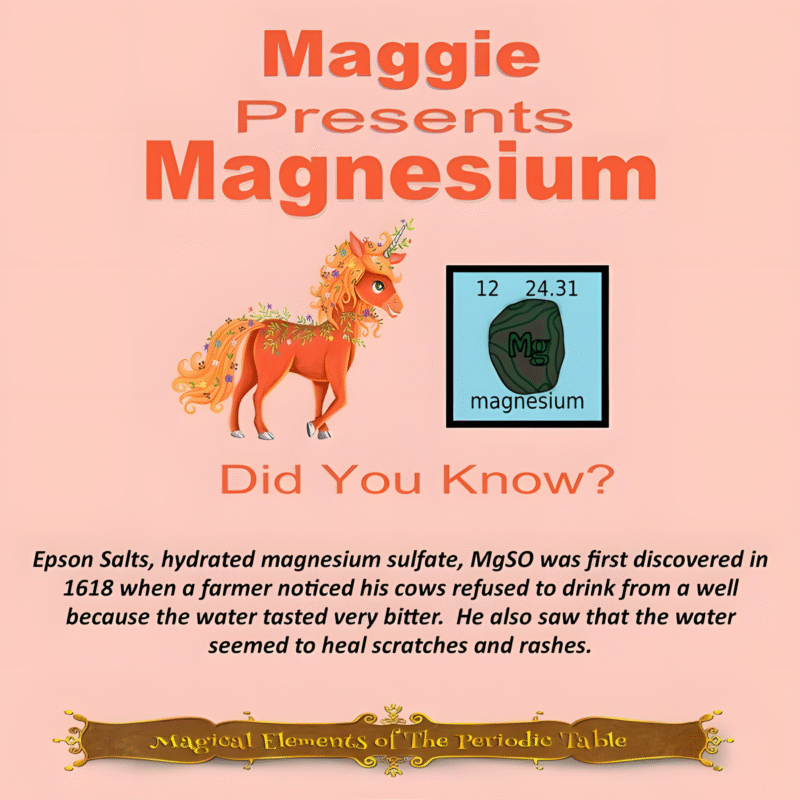
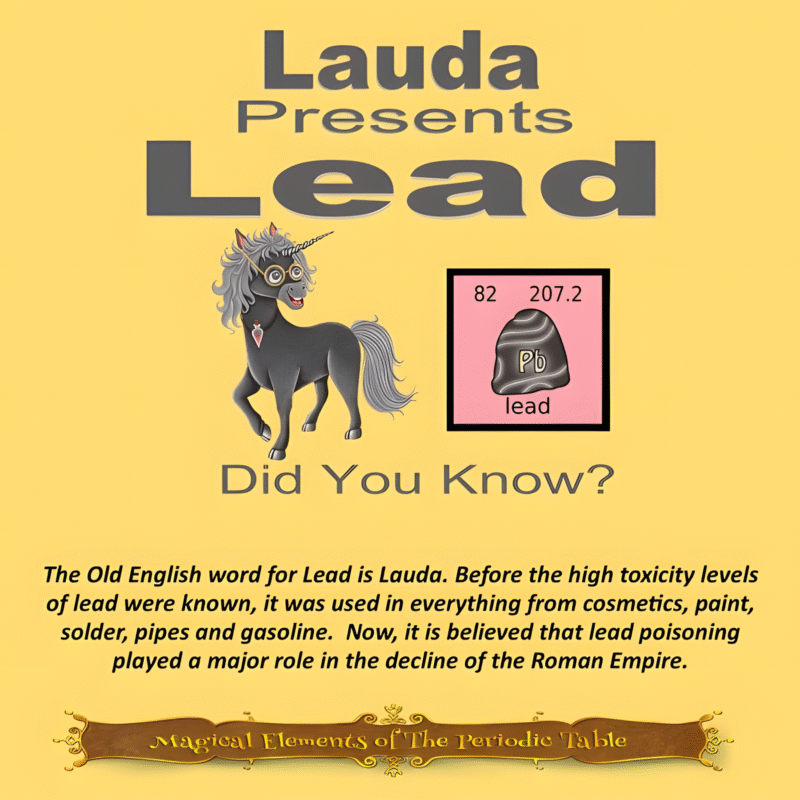
This article is brought to you by Sybrina Durant, the author of the middle grade picture book, Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically By The Metal Horn Unicorns. Learn More. In that book Copper is presented by the unicorn, Cuprum.
Inter-Active Elemental Fantasy-Themed Periodic Table from Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented By The Magical Elementals
Click here to use This Inter-Active Viewer To Learn More About The Elements Each Elemental Represents On This Periodic Table. Want this in a 24″ x 36″ Poster? Click here.
Sybrina Publishing Offers Fun Activities Based On The Book
Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Magical Elementals
Browse Magical Elemental Activities at MagicalPTElements or Sybrina-Publishing on TPT or Classful