The Origin and Commercial Production of Sulfur: Exploring Nature’s Elemental Riddle

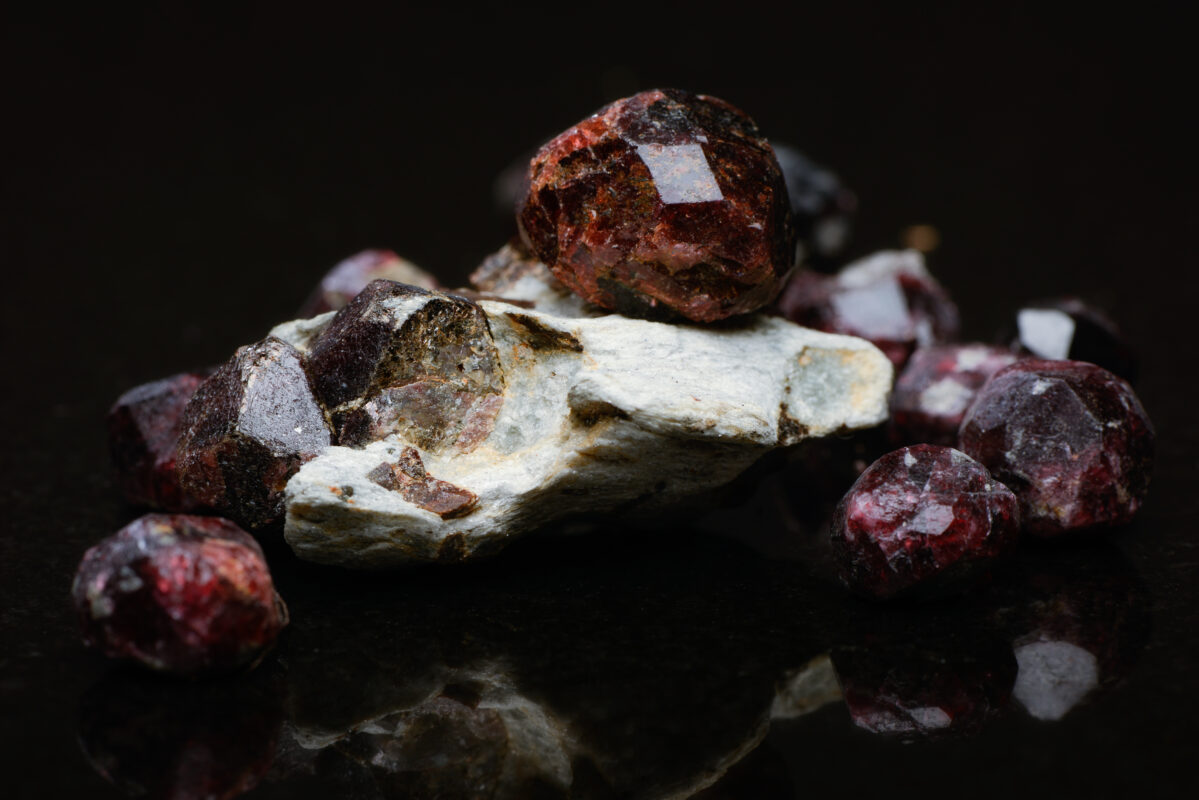
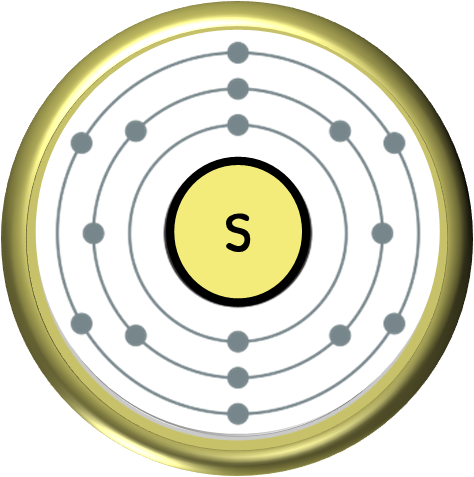
Sulfur, denoted by the chemical symbol “S,” is a naturally occurring element known for its distinct yellow color and strong odor. The origins of sulfur can be traced back to the Earth’s primordial stages, where it emerged through a unique set of geological and biological processes. In this article, we will delve into the origin of sulfur, its occurrence in nature, its extraction and mining processes, commercial processing methods, major sulfur-producing countries, and the environmental implications of sulfur mining.
In its pure form, sulfur is rarely found in nature. Instead, it occurs as various compounds, most commonly as a mineral called pyrite or as sulfate minerals such as gypsum and barite. Pyrite, also known as “fool’s gold,” is a complex iron sulfide mineral with the formula FeS2, while gypsum is a hydrated calcium sulfate mineral (CaSO4·2H2O). These compounds are abundant in certain geological formations and serve as important sources of sulfur.
The extraction and mining processes for sulfur are diverse and depend on the specific source material. The most common method of sulfur extraction is through the mining of sulfur-rich deposits. Sulfur deposits are generally found near volcanic regions, coal beds, oil and gas reserves, and salt domes. In the past, sulfur was mined manually, with workers extracting solid sulfur from the ground by breaking the rock formations containing the mineral. However, modern techniques have evolved, and mining is now predominantly carried out through conventional mining methods or through drilling wells into sulfur-rich deposits.
The commercial processing of sulfur involves several stages. Once mined, sulfur undergoes a purification process to remove impurities and refine it for commercial use. Initially, the sulfur is melted to remove any accompanying materials, such as rock and clay, producing a molten sulfur stream. This molten sulfur is then subjected to further purification, using processes like fractional distillation and chemical treatment, to achieve high purity levels. The end product is predominantly solid sulfur, which is further processed into various forms for commercial use – from elemental sulfur in granules or flakes to sulfuric acid and derivatives.
When it comes to the global production of sulfur, several countries contribute significantly. However, the largest sulfur-producing country is the United States. The U.S. possesses abundant sulfur reserves, primarily found in Louisiana and Texas. Other significant sulfur-producing countries include Canada, Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia. Additionally, countries like Japan, Germany, and South Korea contribute to global sulfur production by importing raw sulfur and refining it for commercial use.
The environmental impact of sulfur mining and processing is a topic of concern. Sulfur extraction from the ground and its commercial production have potential implications for the environment. Mining activities can disrupt ecosystems in sulfur-rich areas, leading to habitat fragmentation and loss of biodiversity. Moreover, the release of sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere during processing and combustion of sulfur can contribute to air pollution and acid rain, negatively affecting human health and ecosystems. Consequently, efforts are made to minimize these impacts through stringent regulations, improved mining practices, and the use of advanced emission control technologies at sulfur processing facilities.
Sulfur plays a crucial role in various industries, making it an essential commodity in the global market. Its applications span diverse sectors, including agriculture (as a component of fertilizers), petroleum and gas processing (for hydrocarbon purification), pharmaceuticals (as an ingredient in medications), and paper manufacturing (as a bleaching agent). This versatility and demand contribute to the extensive commercial production of sulfur worldwide.
While sulfur occurs naturally as compounds and is extracted from various geological sources, it is the commercial processing and production that ultimately make it available for widespread use. The mining and refining of sulfur have evolved over time, with technologies constantly improving to minimize environmental impacts. Understanding the origins and commercial production of sulfur helps shed light on the significance of this element in shaping modern society and the ongoing efforts to ensure its sustainable extraction and processing.
This article is brought to you by Sybrina Durant, the author of the middle grade picture book, Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically By The Elemental Dragons. Learn More. In that book Sulfur is presented by the dragon, Xoe.
Inter-Active Elemental Fantasy-Themed Periodic Table from Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically by The Elemental Dragon Clan
Click here to use This Inter-Active Viewer To Learn More About The Elements Each Elemental Represents On This Periodic Table. Want this in a 24″ x 36″ Poster? Click here.
Sybrina Publishing Offers Fun Activities Based On The Book
Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Magical Elementals
Browse Magical Elemental Activities at MagicalPTElements or Sybrina-Publishing on TPT or Classful