The Origin of Hydrogen: A Key Element in Our World

Hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, plays a crucial role in numerous fields, including energy production, transportation, and research. But where does hydrogen come from? Does it occur naturally as a pure element? This article aims to explore the origin of hydrogen, its extraction methods, commercial processing, and its impact on global economies and the environment.
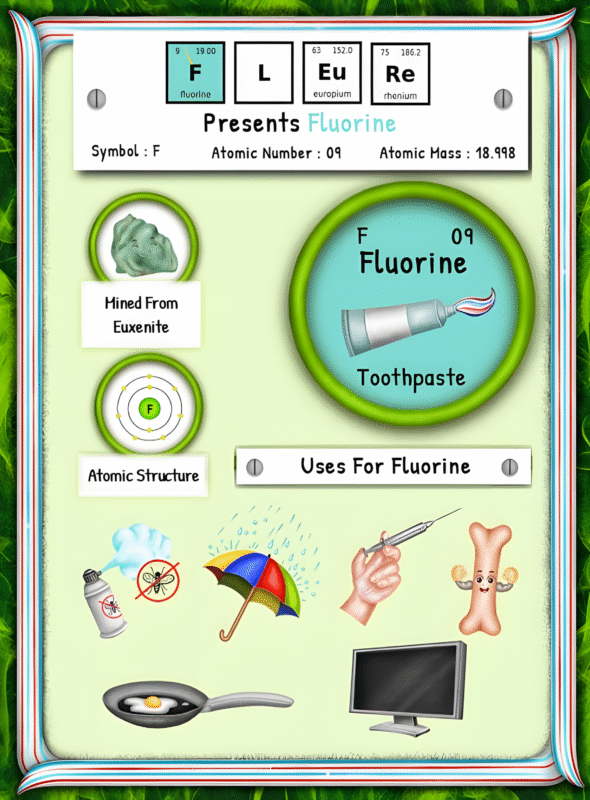
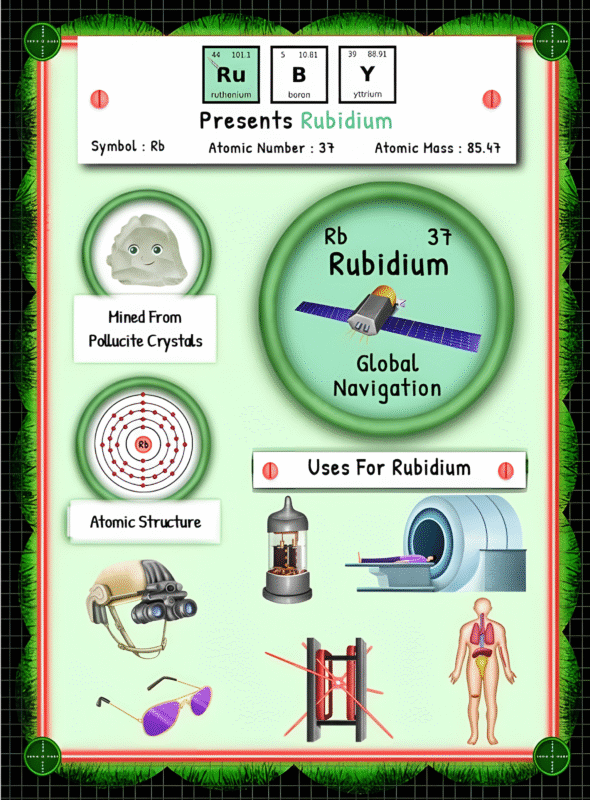
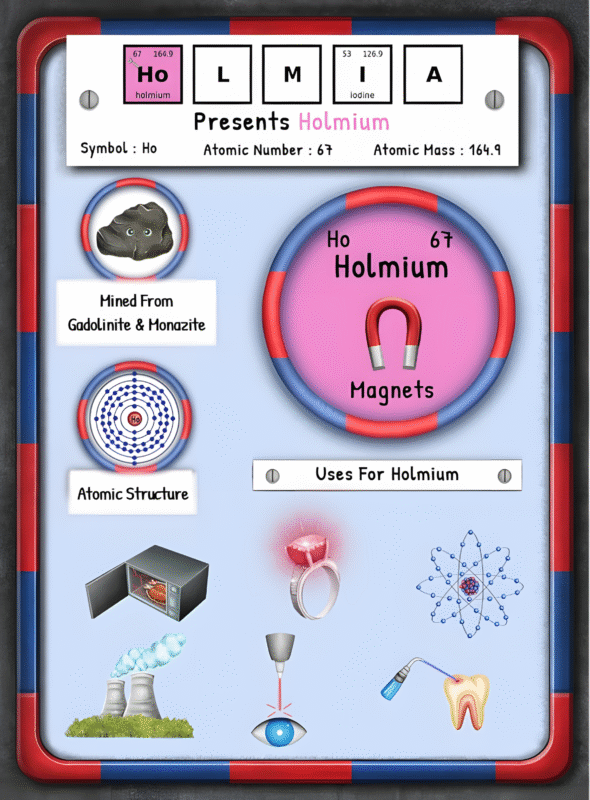
Hydrogen rarely occurs as a pure element in nature. Instead, it typically exists in combination with other elements such as oxygen in water (H2O) or carbon in hydrocarbons. To obtain hydrogen in its pure form, it must be separated from these compounds through various extraction methods.
One of the primary methods of hydrogen extraction is steam methane reforming (SMR). This process involves heating natural gas, primarily methane, with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Natural gas, a fossil fuel, is commonly found deep within the Earth’s crust and is extracted through drilling techniques.
Another popular method of hydrogen extraction is electrolysis, which separates hydrogen and oxygen in water using an electric current. While this process allows for extraction directly from water, it requires significant amounts of electricity, making it less energy-efficient when produced from fossil fuel-based sources.
Hydrogen can also be obtained through other sources, such as biomass gasification or byproduct hydrogen from chemical production. Biomass gasification involves converting organic materials, such as agricultural waste or wood, into a gas, which can then be processed to obtain hydrogen.
Once extracted, hydrogen undergoes commercial processing to increase its purity and usability. This involves removing impurities such as carbon dioxide, sulfur compounds, and trace elements to meet industry standards. The purification process typically includes various techniques, such as pressure-swing adsorption or membrane separation, to obtain high-purity hydrogen.
When it comes to mining hydrogen, it is crucial to note that hydrogen mining is not a physical extraction from the Earth’s crust, like mining for minerals or metals. Instead, hydrogen extraction involves sourcing it from available compounds through chemical processes. As a result, traditional mining methods do not apply directly to hydrogen.
As for the country that mines the most hydrogen sources such as natural gas, it is difficult to attribute specific rankings, as most countries source natural gas for domestic and commercial use rather than specifically for hydrogen extraction. However, countries with significant natural gas reserves, such as Russia, the United States, and Iran, are likely to be leading contributors.
In terms of commercial hydrogen production, China stands out as the largest producer globally, driven by its rapid industrial growth and increasing demand for hydrogen. China produces hydrogen through various methods including coal gasification, SMR, and electrolysis. Japan and the United States are also significant contributors to the commercial production of hydrogen.
The impact of hydrogen production on the environment varies depending on the extraction method and the energy sources used during production. While hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, the majority of hydrogen currently comes from fossil fuels. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with its production and use becomes a significant concern.
Furthermore, the extraction of fossil fuels, such as natural gas, can have detrimental effects on the environment, including methane leaks during drilling and transportation, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Countries heavily reliant on hydrogen production from fossil fuels must address these environmental concerns through the implementation of cleaner extraction and production methods.
The origin of hydrogen lies far beyond a simple extraction process; it is intricately connected to the global energy landscape and environmental sustainability. Companies and governments around the world must continue to invest in research, development, and implementation of clean and efficient hydrogen production methods to reduce the industry’s impact on the environment.
As the world becomes increasingly interested in decarbonization and achieving a more sustainable future, hydrogen is likely to play an even more critical role in our energy systems. By understanding the origin and production processes of hydrogen, we can work towards harnessing its potential as a clean energy source while minimizing its impact on the environment.
This article is brought to you by Sybrina Durant, the author of the middle grade picture book, Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically By The Elemental Dragons. Learn More. In that book Hydrogen is presented by the dragon, Hildy.
Inter-Active Elemental Fantasy-Themed Periodic Table from Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically by The Elemental Dragon Clan
Click here to use This Inter-Active Viewer To Learn More About The Elements Each Elemental Represents On This Periodic Table. Want this in a 24″ x 36″ Poster? Click here.
Sybrina Publishing Offers Fun Activities Based On The Book
Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Magical Elementals
Browse Magical Elemental Activities at MagicalPTElements or Sybrina-Publishing on TPT or Classful