The Origin of Molybdenum: A Rare and Essential Element

Molybdenum, symbolized by the chemical abbreviation Mo, is a rare and versatile metallic element that has played a significant role in various industries since its discovery in the late 18th century. With its remarkable properties, including high melting point and corrosion resistance, molybdenum has found applications in fields ranging from steel production to energy generation. Understanding the origin of molybdenum, its extraction, processing, and mining impact is vital to appreciate its importance in our modern world.
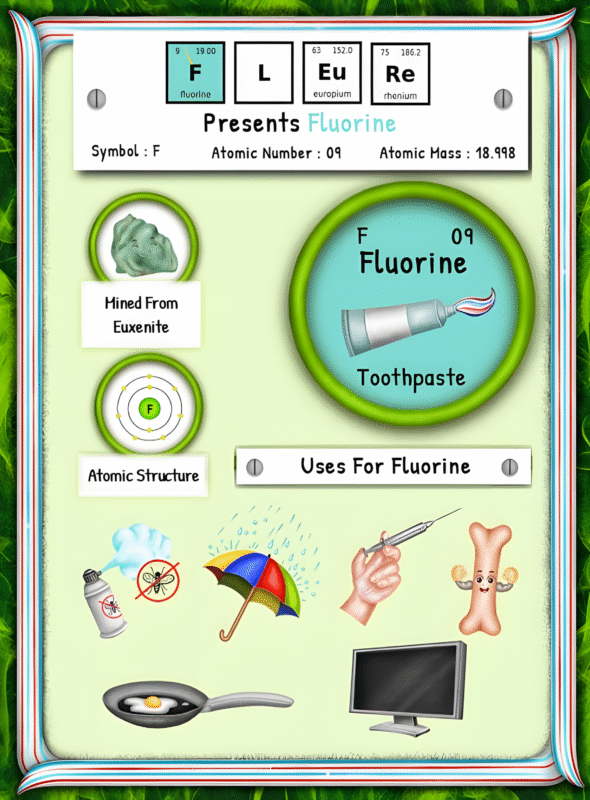
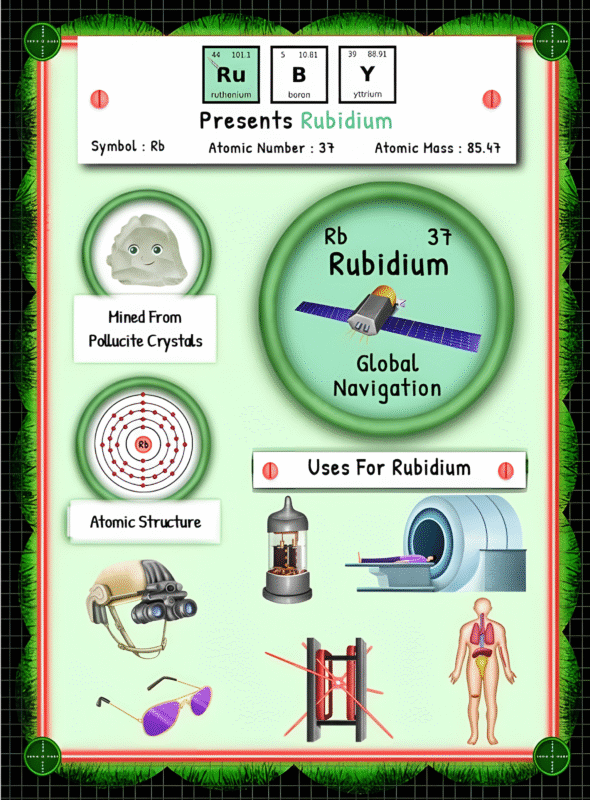
Molybdenum does not occur abundantly in nature as a pure element. However, it can be found in numerous minerals, the most common being molybdenite (MoS2). Molybdenite is a compound that consists of molybdenum and sulfur, and it is the primary source of molybdenum extraction worldwide. The presence of molybdenum in these minerals is the result of a complex geological process that involves both igneous and hydrothermal activities.
The mining process of molybdenum involves several stages, beginning with exploration and prospecting. Geologists search for mineral deposits that have a high concentration of molybdenite. Once a potential site is identified, the second step is the extraction of the ore. This involves drilling, blasting, and transporting the materials to the surface.
After the molybdenite ore is extracted, it undergoes a series of beneficiation processes to separate the valuable mineral from other impurities. Typically, the ore is crushed and ground to a fine powder, followed by flotation, where bubbles adhere to the molybdenite particles and carry them to the surface for further separation. The final stage of processing involves roasting and smelting, which converts molybdenite concentrate into a pure form of molybdenum known as molybdenum oxide (MoO3).
Once molybdenum oxide is produced, it is commercially processed to meet industrial requirements. The most common form of processing is the production of ferromolybdenum, an alloy of iron and molybdenum. Ferromolybdenum is used primarily in the manufacturing of steel, as it enhances its strength and resistance to corrosion. Another method of processing involves converting molybdenum oxide into molybdenum metal, which finds applications in the aerospace and electrical industries.
China is the largest producer of molybdenum, with its vast reserves and extensive mining operations. The country accounts for over 40% of global molybdenum production, primarily extracting the element from its numerous mines and smelting facilities. While this dominance has brought economic benefits to China, it has also impacted the country’s environment. The molybdenum mining process can lead to the release of sulfur and other pollutants, which contribute to air and water pollution. Additionally, the extraction and waste disposal practices associated with molybdenum mining can result in the degradation of natural habitats and ecosystems.
Apart from China, other significant molybdenum-producing countries include the United States, Chile, Peru, and Mexico. These nations also contribute to global molybdenum supplies but to a lesser extent. However, the environmental impact of molybdenum mining is not limited to China alone and can affect these countries as well. In conclusion, molybdenum, despite its rarity in pure form, is a crucial element for modern industries. It is predominantly extracted from molybdenite ores through a mining process that involves beneficiation, roasting, and smelting. China currently dominates worldwide molybdenum production, with environmental concerns arising due to mining activities. Understanding the origin, extraction process, and environmental impact of molybdenum mining is essential to ensure sustainable practices and minimize its ecological footprint.
This article is brought to you by Sybrina Durant, the author of the middle grade picture book, Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically By The Elemental Dragons. Learn More. In that book Molybdenum is presented by the dragon, Maximo.
Inter-Active Elemental Fantasy-Themed Periodic Table from Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically by The Elemental Dragon Clan
Click here to use This Inter-Active Viewer To Learn More About The Elements Each Elemental Represents On This Periodic Table. Want this in a 24″ x 36″ Poster? Click here.
Sybrina Publishing Offers Fun Activities Based On The Book
Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Magical Elementals
Browse Magical Elemental Activities at MagicalPTElements or Sybrina-Publishing on TPT or Classful