The Origin of Xenon: A Unique Element

Xenon is a fascinating element that has captured the curiosity of scientists and enthusiasts alike for many years. With its unique properties and applications, it is worth exploring its origin, occurrence in nature, extraction process, commercial processing, and production.
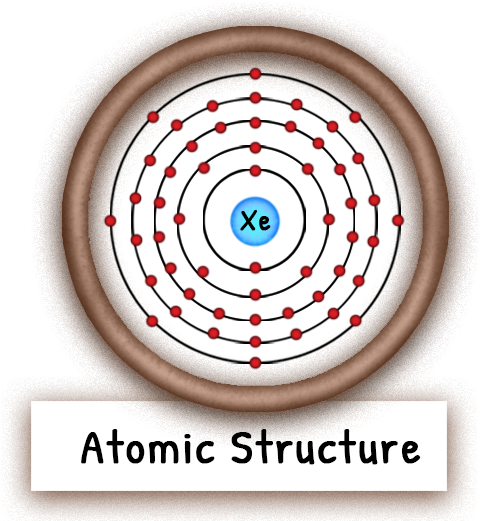
First discovered in 1898 by Scottish chemist Sir William Ramsay and English chemist Morris Travers, xenon is a noble gas found in the Earth’s atmosphere in trace amounts. However, it does not occur naturally as a pure element. In fact, xenon is found in the atmosphere, soil, and waters due to its production from radioactive decay. This means it is formed as a result of decay from other elements present in the earth’s crust.
While xenon occurs naturally, it is challenging to extract it in significant quantities due to its low abundance. Its mining process involves the extraction of gases from air, specifically the separation of xenon gas from other atmospheric gases. This extraction process can be accomplished through cryogenic distillation, in which air is cooled to very low temperatures to freeze and separate the different gases present. Through several stages of distillation, xenon can be obtained in a pure state.
Commercially, xenon is primarily extracted from the air using large-scale cryogenic distillation plants. The complexity of the process and the need for specialized equipment makes it a relatively expensive procedure. As a result, the commercial production of xenon is limited to areas that have a demand for it, particularly in industries such as lighting, electronics, and medical imaging.
When it comes to xenon production, the largest mining and production country is China. China’s dominance in xenon production can be attributed to its vast rare earth reserves, which are home to several xenon-rich sources. The country produces and exports the majority of the world’s xenon, making it a significant player in the global market.
However, the mining and production of xenon can have environmental implications. Mining rare earth elements, including sources of xenon, often involves intensive processes that can lead to environmental degradation. China, for instance, has faced significant challenges in managing the environmental impact of rare earth element mining. The extraction and processing of these elements can result in soil and water pollution, as well as the destruction of ecosystems.
Despite these challenges, efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of xenon extraction and production. These include the implementation of more sustainable mining practices, stricter regulations, and improved waste management systems. Additionally, technological advancements in extraction and processing techniques are also helping to reduce the environmental footprint associated with xenon production.
In terms of commercial production, China’s dominance undoubtedly affects the global market. With its large-scale production capacity, China not only meets its domestic demand but also supplies xenon to other countries. While the exact production figures may vary, China’s substantial production capabilities impact pricing, availability, and overall market dynamics. Other countries, such as Russia and the United States, also contribute to xenon production, but to a lesser extent.
In conclusion, xenon is an intriguing element with origins in the Earth’s atmosphere and soil due to radioactive decay. Although it does not occur naturally as a pure element, its extraction process involves separating it from atmospheric gases through cryogenic distillation. The commercial processing of xenon is primarily carried out in countries like China, which possesses ample reserves of xenon-rich sources. However, the mining and production of xenon can have environmental consequences, with China facing challenges related to environmental degradation. Efforts are being made to mitigate these issues and ensure more sustainable practices in the future.
This article is brought to you by Sybrina Durant, the author of the middle grade picture book, Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Alphabetically By The Metal Horn Unicorns. Learn More. In that book Xenon is presented by the unicorn,Xena.
Inter-Active Elemental Fantasy-Themed Periodic Table from Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Presented Magical Elementals
Click here to use This Inter-Active Viewer To Learn More About The Elements Each Elemental Represents On This Periodic Table. Want this in a 24″ x 36″ Poster? Click here.
Sybrina Publishing Offers Fun Activities Based On The Book
Magical Elements of the Periodic Table Magical Elementals
Browse Magical Elemental Activities at MagicalPTElements or Sybrina-Publishing on TPT or Classful